
Lenses to gather and focus light, reflective telescopes use mirrors to do the Reflection: Mirror Mirror In the Tube Image Source: Krishnavedala The image quality is good overall and perfect for in solar system observation. There are even ways to try and fix chromatic aberration but they can be complicated or pricey depending on the option. Eyepieces can be bought and configured for different levels of viewing and magnification. Overall, refractive telescopes are simple, proven and customizable. The light from some of these observable stars left their origin point at the time of the Roman Empire! It is wild to think about light coming off of stars hundreds or thousands of light-years away, passing through vast distances of space and being split up in a telescope on earth and hitting a human eye after who knows how long? While this is more distracting than anything it does affect the image quality of refractive images, especially bright ones. It creates a rainbow glow around objects which is due to the light being split up as it passes through the lens. White light, like the light from stars, can be split into many different colors when refracted.Ĭhromatic aberration occurs when looking at bright objects through the lens. Since refraction is based on bending light it creates a distortive effect which is called chromatic aberration.Īnyone who has seen a rainbow or messed around with a prism in their life is familiar with the idea of chromatic aberration. Their biggest downside has to do with image quality, which has to do with the physics of refraction. They have been around in some form for over 400 years and they are based on proven science. Refracting telescopes are relatively easy to use, they are easy to find and they work. Scientific and commercial telescopes have massive objective lenses to gather as much light as possible. To get the highest resolution possible when viewing the sky, you want the largest light gathering potential possible which is directly related to the size of the objective lens. A low-resolution image will remain low resolution even if you continue to zoom in on it and in a lot of cases magnifying a low-resolution image makes the resolution worse. Magnification is important but so is image clarity. It’s not all about the MagnificationĪ common belief is that magnifying power is the most important aspect of a telescope. The objective lens will usually be a static piece of a refracting telescope with the option to change out different size eyepieces to get different magnification levels.įor example, a large magnification is not necessary when looking at the moon compared to trying to see the rings of Saturn. Refracting magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by the focal length of the eyepiece lens. Lenses and is the one which would be pointed at the sky. The objective lens is the larger of the two Unlike glasses, refracting telescopes usually have two lenses: the objective lens and the eyepiece. Refracting telescopes work on the same principle but they are trying to gather images from much farther away and therefore must be much larger. Glasses are designed to correct certain vision problems usually at a distance of about twenty feet from the wearer. These lenses are made specifically to certain shapes to capture light and create a desired magnifying effect. Refraction is the magnification method that uses curved glass or plastic to capture light and magnify the desired image.
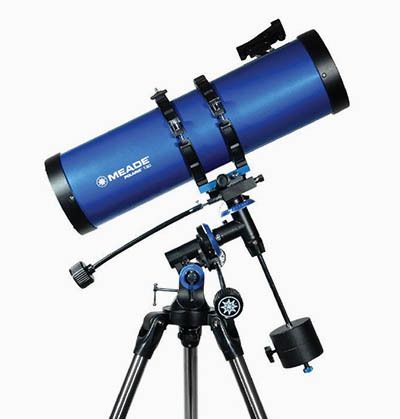

The most common kind of refraction that is observable in daily life are glasses and contacts.

So how does each work and is one better than the other? Refraction: Lend Me Your Lens Image Source: Szőcs Tamás Today, both kinds of telescopes can be widely found in scientific and casual settings. The first telescopes were refracting in nature and were later adapted to have a reflective variant.
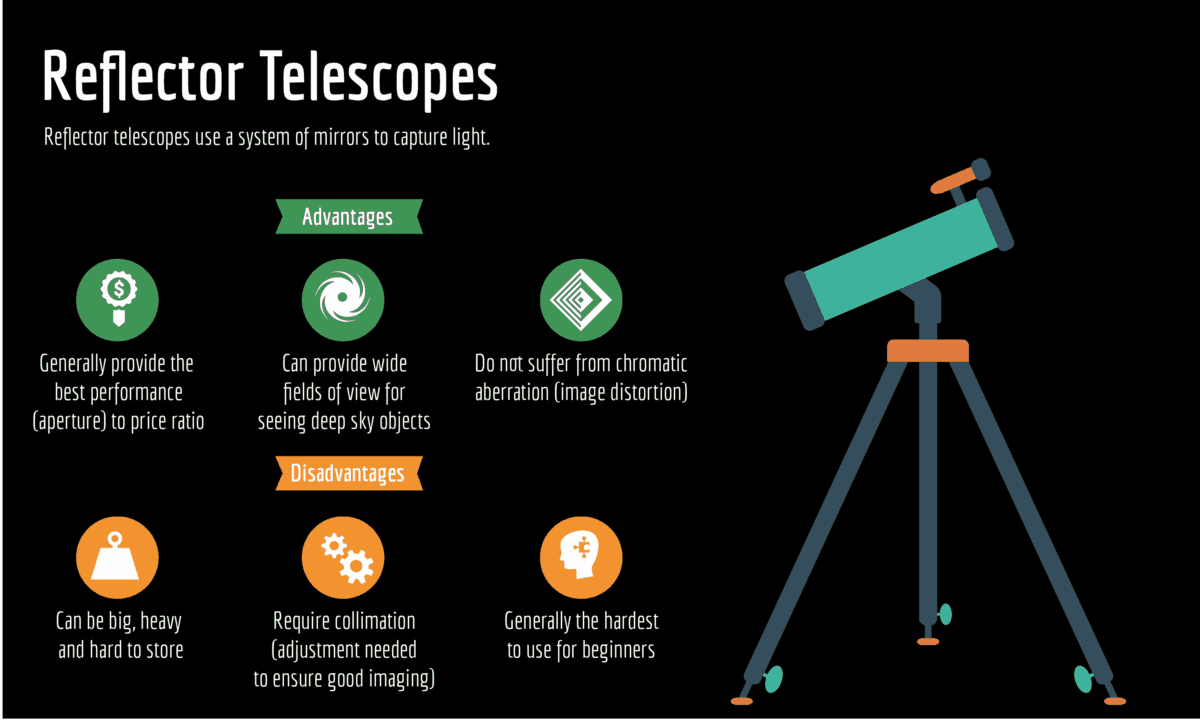
Both kinds of telescopes use different methods to achieve this same goal. In both reflecting and refracting telescopes, light is gathered and focused on a single point where a human eye can see it better than it could on its own. Telescopes work on the principle of magnifying a distant object in a way that is clear and natural to observe.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
